The following two are the defining characteristics of VPN’s –
- VPN just basically means the extension of Private network over a Public network.
- VPN does NOT imply encryption although almost all VPN’s use it.
Examples are –
- L2 VPN’s – Ethernet VLAN, QinQ, Frame Relay, VPLS etc.
- L3 VPN’s – GRE Tunnel, MPLS Tunnel, IPsec etc.
FYI – MPLS VPN has nothing to do with security. It is provisioned by SP’s to connect multiple customer sites together for L3. You can use VPN that provides security like IPsec on top of it maybe. The core functionality of VPN is simply to extend a private network over the public infrastructure. Extension simply means giving one private network an illusion that the remote private network is actually NOT remote, just like an RPC. IPsec is useful because we do not need SP provisioning unlike MPLS L3VPN. Also IPsec provides both site-to-site and remote access VPN. Therefore it has an Always-On and Dial-On-Demand option respectively. And most importantly it provides encryption
https://www.vpnmentor.com/blog/remote-access-vpn-vs-site-to-site-vpn-full-guide/
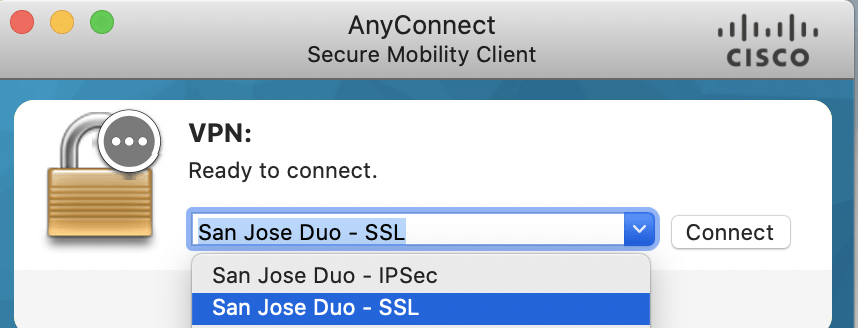
Cisco AnyConnect Remote access VPN shows 2 types of remote access technologies – SSL and IPsec. IPsec secures the IP Payload [ L4 – L7 ] and SSL secures just the Application layer [ L7 ].